Quantum Computing: Transforming the Future of Technology
Introduction
What if today's most potent machines could resolve issues that would take hundreds of years in only a few seconds? Quantum computing promises to fulfill this promise, and it's not just science fiction. This blog will go into the foundations of quantum computing, its innovative uses, and its potential to completely transform businesses around the world.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a cutting-edge technology that represents data using ideas from quantum physics, the study of the tiny. Unlike classical computers, which utilize bits to represent data as 0s or 1s, quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in several states concurrently due to a phenomenon called superposition. Consequently, quantum computers can now do complex calculations at unprecedented speeds.
Example: Imagine flipping a coin. A classical bit would represent the coin as either a head (1) or a tail (0). A qubit, however, can represent a state where the coin has both heads and tails simultaneously.

Key Concept:
Entanglement: A phenomenon where qubits become interconnected, so the state of one qubit instantly affects the state of another, regardless of distance.
Quantum Gates: Operations that manipulate qubits, forming the building blocks of quantum algorithms.
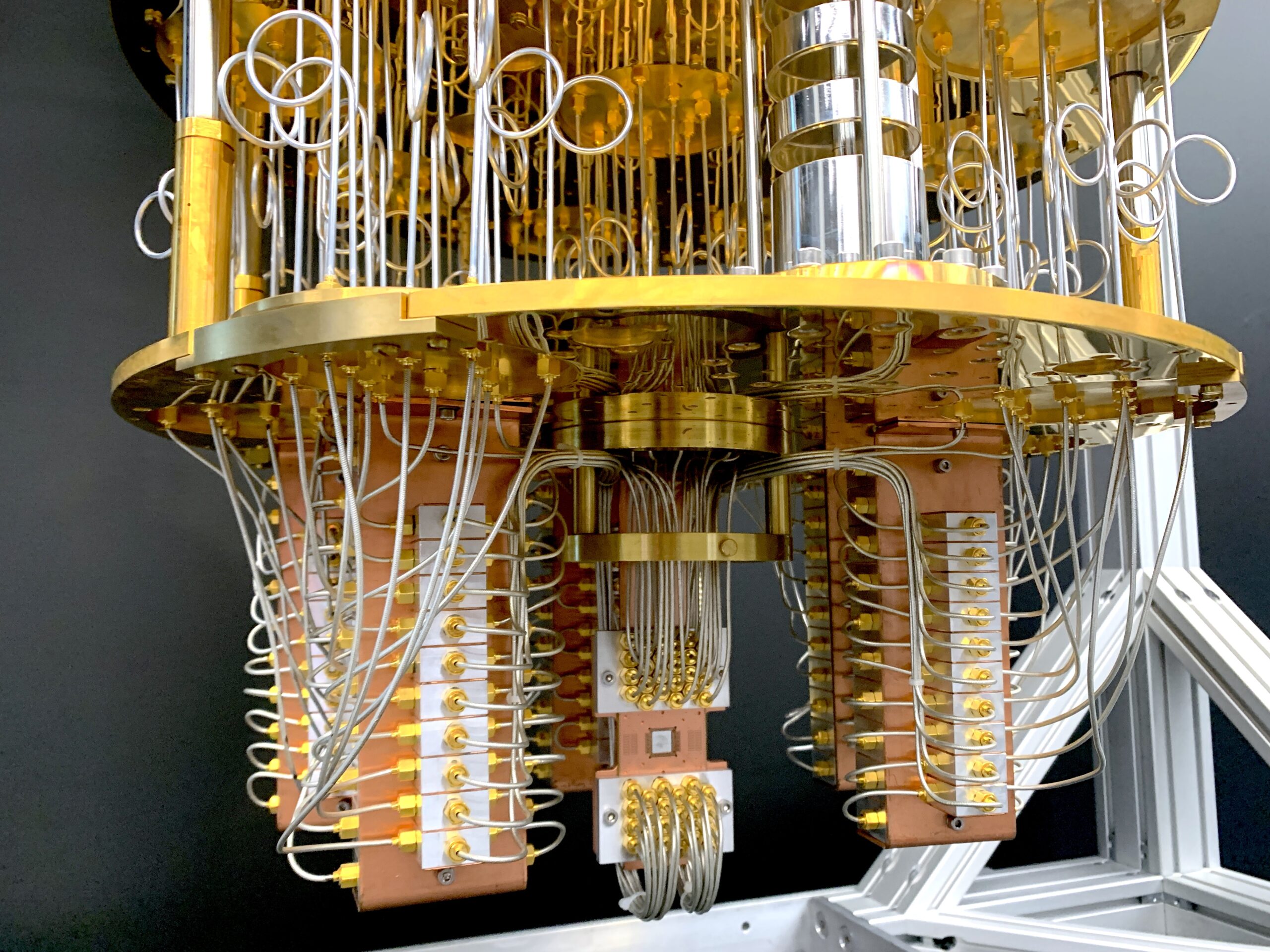
How Does Quantum Computing Work?
In essence, quantum circuits—which are made up of qubits controlled by quantum gates—are the foundation of quantum computing. These gates take advantage of the special characteristics of quantum mechanics to allow the computer to analyze several responses at once.
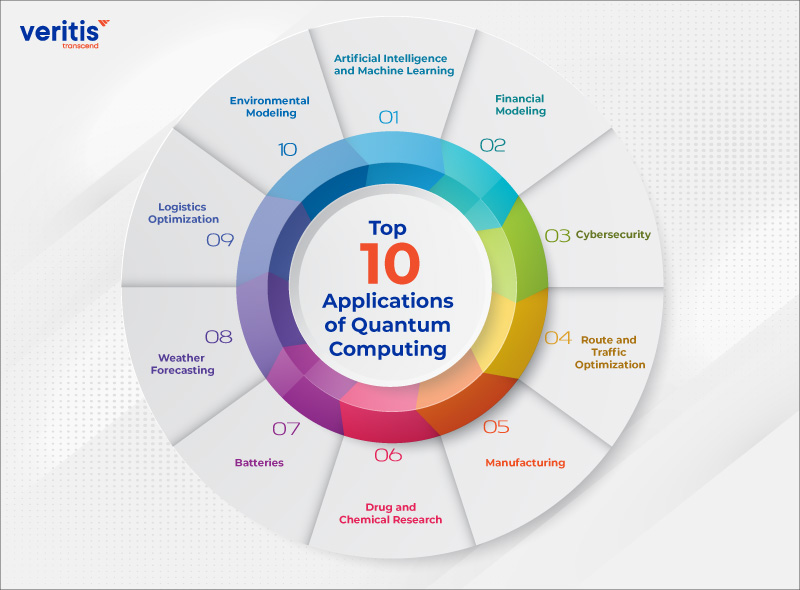
Applications of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is poised to revolutionize various fields:
Drug Discovery: Simulating molecular interactions to accelerate the development of new medicines.
Cryptography: Breaking traditional encryption methods while enabling more secure quantum encryption.
Artificial Intelligence: Enhancing machine learning algorithms with faster data processing.
Financial Modeling: Optimizing portfolios and predicting market trends with unparalleled accuracy.
Climate Modeling: Solving complex simulations to better understand and combat climate change.
Example: Google’s quantum computer, Sycamore, achieved quantum supremacy by solving a problem in 200 seconds that would take classical supercomputers thousands of years.
Challenges and Limitations
While promising, quantum computing faces significant hurdles:
Error Rates: Qubits are extremely sensitive to their environment, leading to errors.
Scalability: Building and maintaining stable quantum systems is complex and costly.
Resource Requirements: Quantum computers require ultra-cold environments to function.
Quote: “Quantum computing is like a rocket ship: powerful, but we’re still figuring out how to steer it.”
Future of Quantum Computing
As researchers overcome current challenges, quantum computing is expected to:
Democratize access through cloud-based quantum platforms.
Accelerate technological breakthroughs across industries.
Create entirely new markets and business models.
Major players like IBM, Google, and Microsoft are leading the charge, investing heavily in quantum research and development.
Conclusion
A paradigm change in technology, quantum computing holds promise for solving the most difficult issues facing humanity. The rate of invention indicates that a quantum-powered future is closer than we may believe, even though there are still problems to be resolved. As we continue to explore this fascinating frontier, be sure to return.
Subscribe to our blog for more insights into emerging technologies like quantum computing. Let’s shape the future together!
Comments
Post a Comment